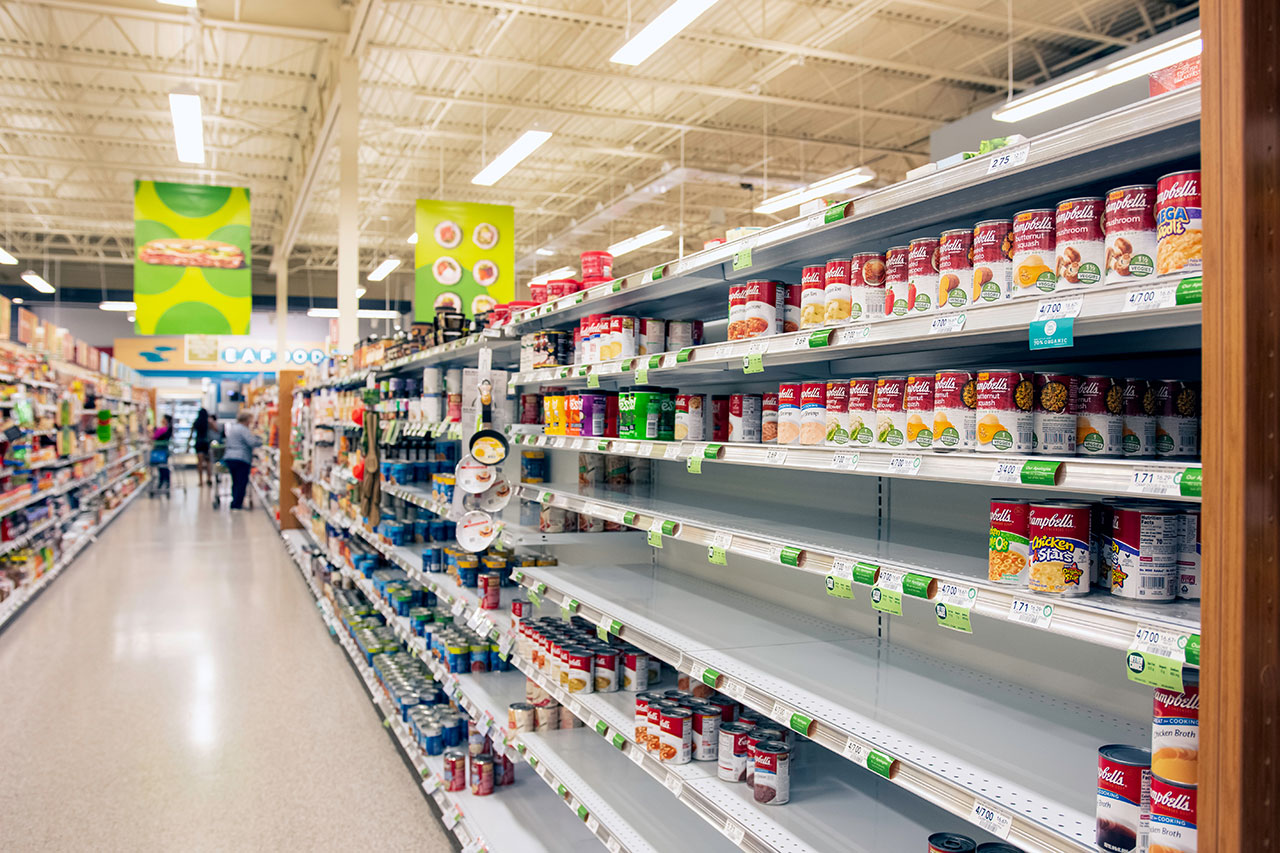
Scarcity, the idea that access to a given resource is limited thereby driving up that resource’s value, is one of the most basic and proven marketing strategies available. Today we will talk about what scarcity is, how it works and how it can effectively be put into practice in B2B marketing.
Utilizing Scarcity Effectively in B2B Marketing – Video summary
For the full article scroll below.
What is scarcity?
Scarcity is the idea that when a good or service is in short supply, or scarce, it is more desirable than when it is plentiful. Many scientific studies that have shown this in action as part of human behavior (Feinberg, 2015). One of the most well-known scarcity studies simply evaluated how much worth a person placed on a cookie in two instances; one where there were ten cookies to choose from and one where there were only two cookies to choose from (Worchel, Lee, & Adewole, 1975). The cookies that were scarce were valued higher than the cookies that were abundant, clearly showing how people view objects in short supply differently.
The way people think about scarcity is considered a heuristic, or a strategy used by the human brain to generalize and expend less energy and time when making a decision. When a resource is less available, people can feel stress or fear that they will miss out on an item or opportunity, which leads them to use these mental shortcuts.
How scarcity works
The scarcity heuristic works because it taps into the emotional centers of the brain. Chemically speaking, scarcity causes glucose levels in the frontal cortex of the brain, which is responsible for complex cognitive functions like decision making, to drop. This means that it can’t do its job as well, so people are more likely to rely on mental shortcuts or make faster, less thought-out decisions. This is similar to when you get overwhelmed with work or relationship stress so you don’t have the mental self-control to stick to healthy eating and perhaps buy a pizza or bucket of ice cream when you would otherwise choose a salad. The stress caused by scarce resources causes people to exercise less control rather than responsibly thinking about their spending and personal resources.
Another way that scarcity connects to human emotions is that when someone possesses an item that is scarce they feel special or powerful, which makes the item even more desirable to those who don’t have it. Feelings of envy and the desire for people to possess what they don’t have, sometimes called commodity theory, is a powerful emotional part of how scarcity influences people to perceive items as having increased value (Brock, 1968).
Actual versus artificial scarcity
Because the brain’s mechanisms for processing and responding to scarcity have been built up evolutionarily, they occur in situations where there is any perceived scarcity, either real or artificial.
Scarcity in marketing
Scarcity is utilized in marketing by creating the sense of urgency that will encourage customers to act quickly rather than wait to purchase your product. This is done in two main ways: a limited amount of product, and a limited amount of time. Below we will look at some examples of how this can be done.
Scarcity of product
Product scarcity from when a limited number of products or services are available is a great way to create a sense of urgency for buyers. Often this can also increase the value of the product because those in possession are now members of an exclusive group. Here are a few ways that limited products can be implemented:
Limited Supply/High Demand
Creating a limited supply initially can lead to a higher demand and product scarcity. An example of this was when Nintendo underestimated the demand for the Wii console in 2006 (Kohler 2007). With an unexpectedly high demand during its release, consoles sold fast and were highly sought after due to their rarity. The product scarcity caused customers to have heightened interest in the Wii for years after it was released. When supply was able to catch up, they were still selling fast!
Limited edition
One great example of this is to introduce a special version of your product with a limited stock, such as Adidas’ release of a limited edition new color of their Yeezy Boost collection sneaker. This new sneaker was not a new model and cost was the same as other sneakers in the collection—the only difference was the color. But through promoting the sale of their limited edition sneakers well on social media, they were sold out within a minute of the sale opening online (Fowler, 2018).
Scarcity of time
Another way that urgency can be created is through a scarcity of time, where a product, deal, or special offer is only available for a short while. This can also create a sense of exclusivity for customers and intensifies the fear associated with the need to get a product before it is gone. Here are a few examples of how this has been used:
Seasonal or holiday deals
The perfect example of a seasonal deal is Starbucks’ pumpkin spice latte. For only a few short months every year customers can take advantage of this special product. This sense of urgency coupled with active social media engagement about their deals has made the pumpkin spice latte wildly successful for almost two decades (Lobert, 2019).
Limited Sale Time
Sometimes instead of limiting the amount of time that an product is available for, a company can offer a special price, free shipping, or an extra bonus that comes with a product purchase for a limited amount of time. These kinds of sales can also work really well as holiday or special event deals. A good way to mix this up can be to offer a limited time sale on specific products or services that connect to a theme for that period of time. This will be most effective when promoted rigorously both before and during the sale.
Limited Time Free Trial
A limited time free trial is an excellent way to get customers hooked on your services. The limited time trial creates a sense of urgency for a client that will encourage them to use it fully and get a very good feel for how valuable the product or service could be for them long-term.
Real versus implied scarcity
As previously mentioned, creating the feeling of urgency can affect sales even if it isn’t connected to actual shortage of product or time. Real urgency works better than implied urgency, but you can’t always create a real urgency situation. In these cases you can still imply a sense of urgency in several ways:
Language
Without spreading false information, companies can still imply urgency by using words such as “now” or “today” in advertisements.
Social Proof
While you can’t typically control the demand for your products, you can highlight the existing demand to create a feeling of urgency. This makes use of the concept of social proof, where people look to other people’s actions to determine how to behave. Examples of this type of language would be saying “purchased by 5 customers today” or “being used by 20 companies this season.”
When scarcity is ineffective
As previously mentioned, scarcity causes stress on the human brain. Just thinking about a situation where a necessary resource is scarce is enough to drop a person’s cognitive functioning more than if they had stayed awake for 24 hours (Shafir & Mullainathan, 2013). Even when the scarce resources are not necessary for survival and people are in a state of economic abundance, they can still feel enough stress in consumer situations to display aggression; the ultimate example of this being a Black Friday brawl over hugely discounted scarce items (Kristofferson et al., 2017). Moreover, customers do not like to feel like they are being taken advantage of or played with. If a customer has reason to believe that scarcity claims in advertising are manufactured or are simply a sales tactic, then they will not be as effective (Lee et al., 2014). It is important, therefore, to be careful how scarcity marketing tactics are used so as to benefit your company and not frustrate or drive away customers.
Tips for Scarcity Marketing Implementation
Be Authentic
Whenever possible, emphasize actual scarcity in your marketing. Scarcity marketing that shows how much product is left can be a helpful tool that increases transparency between you and your clients. It has the potential to increase sales without making customers feel as if advertising is being forceful or insincere. If nothing is actually scarce, offer shipping deals or implied scarcity that is straightforward and accurate.
Use Moderation
Scarcity marketing in sales is more effective when used for special deals rather than regular, recurring price drops. If customers get used to scarcity marketing from your business then it no longer emphasizes anything special and your client base will realize that it has no meaning. This can also lower perceptions of your company’s trustworthiness in the eyes of your customers.
Implement Gradually and Track Effectiveness for Your Client Base
Every industry and customer population is unique, so it may take some experimentation to find the best ways to use scarcity marketing to help reach your customers. The best way to do this is to observe how similar businesses have implemented scarcity marketing and slowly try approaches that fit your goals. Tracking each strategy’s effectiveness can give you good data to use in building future scarcity marketing plans.
If you’re interested in exploring further academic research being done about scarcity and how it affects people in consumer situations, you can check out http://www.understandingscarcity.com/.